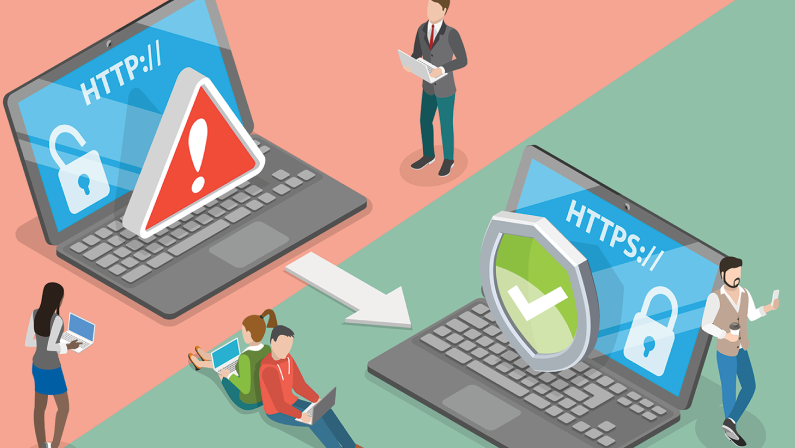
When you browse the internet, you trust that your personal information—like passwords, credit card details, or even your email address—is kept safe. But how does that security work?
That’s where SSL comes in. If you run a business website or just enjoy online shopping, SSL is crucial in protecting your data and ensuring a safe browsing experience.
In this article, we’ll tackle SSL definition, how it works, and why it’s essential for every website.
What is SSL?

What does SSL stand for? SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a security protocol that encrypts the connection between a user’s browser and a website’s server. This encryption ensures that sensitive data—such as login credentials, financial details, and personal information—remains private and secure from hackers or malicious attacks.
Today, SSL has evolved into TLS (Transport Layer Security), the latest version of this encryption technology, but the term “SSL” is still widely used.
How does SSL/TLS work?
SSL/TLS creates a secure, encrypted link between a web server and a browser, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Encryption: SSL/TLS encrypts data transmitted between the website and the user, making it unreadable to cyber criminals. This protects personal details, credit card numbers, and passwords.
- Authentication: It verifies the website’s identity through SSL certificates, ensuring users communicate with the intended site and not a fraudulent one. Websites with SSL display a padlock icon in the browser’s address bar.
- Data Integrity: SSL/TLS ensures that data transferred between the user and the server is not altered or tampered with during transmission. This prevents cyber threats such as data breaches and man-in-the-middle attacks.
Why is SSL/TLS important?
SSL/TLS is essential for protecting user data, ensuring privacy, and building trust with website visitors. Search engines like Google prioritize SSL-secured websites, giving them a ranking boost. Additionally, SSL compliance is crucial for e-commerce sites handling financial transactions, as it reassures customers that their data is safe. Without SSL, websites risk security breaches, loss of customer trust, and potential penalties from search engines or regulatory bodies.
Are SSL and TLS the same thing?
SSL and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are both encryption protocols used to secure internet connections. While SSL was the original standard, it has since been replaced by TLS, which is more secure and efficient. Despite this, many people still refer to website security certificates as “SSL certificates,” even though modern implementations use TLS.
What is an SSL Certificate?

An SSL certificate is a digital certificate that verifies a website’s identity and enables encrypted communication between a web server and a user’s browser. Issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA), it contains essential details like the website’s domain name, the issuing CA, and an expiration date. When installed, it activates HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure), ensuring a secure browsing experience.
Types of SSL and TLS Certificates
SSL and TLS certificates come in different types, each offering varying levels of validation and security. Choosing the right one depends on the website’s needs and the level of trust required.
Extended Validation (EV SSL Certificate)
EV SSL certificates provide the highest level of authentication and security. They require a thorough verification process, including legal and operational checks on the business. Websites with EV SSL display a green address bar or company name in the browser, boosting customer confidence.
Organization Validation (OV SSL Certificate)
OV SSL certificates offer a moderate level of security, verifying the organization behind the website. While they don’t display a green address bar, they still provide trust indicators, such as the company’s name in the certificate details. These certificates are ideal for businesses needing user trust but not handling highly sensitive transactions.
Domain Validation (DV SSL Certificate)
DV SSL certificates provide basic encryption with minimal validation. They confirm domain ownership but don’t verify business details. These certificates are the fastest and most affordable option, commonly used for personal websites or blogs where extensive authentication isn’t necessary.
How to Choose and Obtain an SSL Certificate

Selecting the correct web SSL certificate depends on your website’s security needs and the level of trust you want to establish.
- Assess Your Security Needs: Determine if you need basic encryption (DV), business validation (OV), or the highest level of trust (EV). E-commerce sites and businesses handling sensitive data should opt for OV or EV certificates.
- Choose a Reputable Certificate Authority (CA): Purchase your SSL website security certificate from a trusted CA, such as DigiCert, GlobalSign, or Let’s Encrypt. A well-known provider ensures compatibility with most browsers and devices.
- Install and Maintain Your Certificate: Once purchased, install the certificate on your web server and ensure it remains valid. Regularly renew it before expiration and monitor for potential security vulnerabilities.
SSL Frequently Asked Questions
SSL protocols play an important role in securing online communication, but many still question its relevance and functionality. Below are answers to some of the most common queries regarding SSL and website security.
Is SSL Still Up to Date?
While the term “SSL” is still widely used, SSL itself has been replaced by TLS (Transport Layer Security), which is a more advanced and secure protocol. TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3 are the current standards, offering improved encryption and better protection against cyber threats.
Is SSL More Secure Than HTTP?
Yes, SSL (or more accurately, TLS) encrypts data transmitted between a user’s browser and a website, making it significantly more secure than HTTP. HTTP does not encrypt data, leaving it vulnerable to interception, while HTTPS (secured with SSL/TLS) ensures privacy and data integrity.
What Is the Difference Between Symmetric and Asymmetric Encryption?
Symmetric encryption uses a single key to encrypt and decrypt data, making it fast but requiring secure key sharing. Asymmetric encryption, used in SSL/TLS, involves a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption, providing stronger security for internet communications.
Can an SSL Certificate Be Used on Multiple Servers?
Yes, certain types of SSL certificates, such as Wildcard SSL and Multi-Domain SSL, can be used on multiple servers. Wildcard SSL secures subdomains under a single domain, while Multi-Domain SSL covers multiple distinct domains under one certificate.
Secure Your Website with the Right Digital Partner
Choosing the right SSL certificate is just one part of building a secure and trustworthy online presence. To fully optimize your website for performance, security, and digital marketing success, partnering with experts can make all the difference.
LeadOrigin, a digital marketing agency in San Francisco, CA, specializes in helping businesses create and maintain secure, high-performing websites.
From SSL secure integration and SSL cyber security to SEO, branding, and conversion optimization, our team ensures your website meets industry standards while delivering exceptional user experience.
Ready to secure and grow your online presence? Contact LeadOrigin today to get started!